Developer Guide
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
-
Appendix: Requirements
- Product scope
- User stories
-
Use cases
- Use case: Add a worker (UC-001)
- Use case: Delete a worker (UC-002)
- Use case: Edit a worker’s information (UC-003)
- Use case: Add a shift (UC-004)
- Use case: Delete a shift (UC-005)
- Use case: Edit a shift’s information (UC-006)
- Use case: Assign a worker to a shift (UC-007)
- Use case: Unassign a worker from a shift (UC-008)
- Use Case: Hire a new worker for shifts (UC-009)
- Use case: Calculate the pay earned by a worker for the week (UC-010)
- Use case: View the list of workers who are available to work for a given shift under a given role (UC-011)
- Use case: Add a new role into the McScheduler (UC-012)
- Use case: Delete a role from the McScheduler (UC-013)
- Use case: Edit an existing role in the McScheduler (UC-014)
- Use case: Take leave for a worker for a given shift (UC-015)
- Use case: Cancel leave for a worker for a given shift (UC-016)
- Use case: Reassign the worker to a different role for a given shift (UC-017)
- Non-Functional Requirements
- Glossary
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
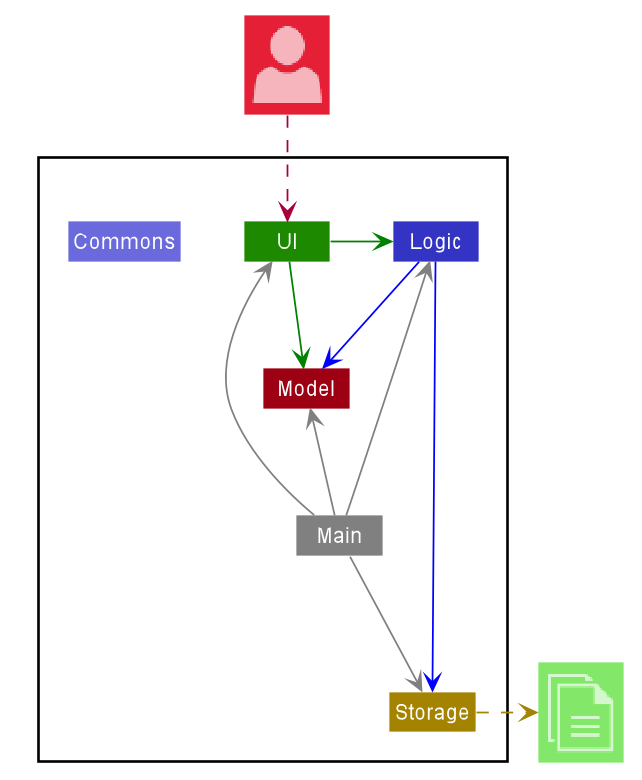
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App. Given below is a quick overview of each component.
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder.
Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Main has two classes called Main
and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Each of the four components,
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - exposes its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which implements the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component (see the class diagram given below) defines its API in the Logic.java interface and exposes its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which implements the Logic interface.
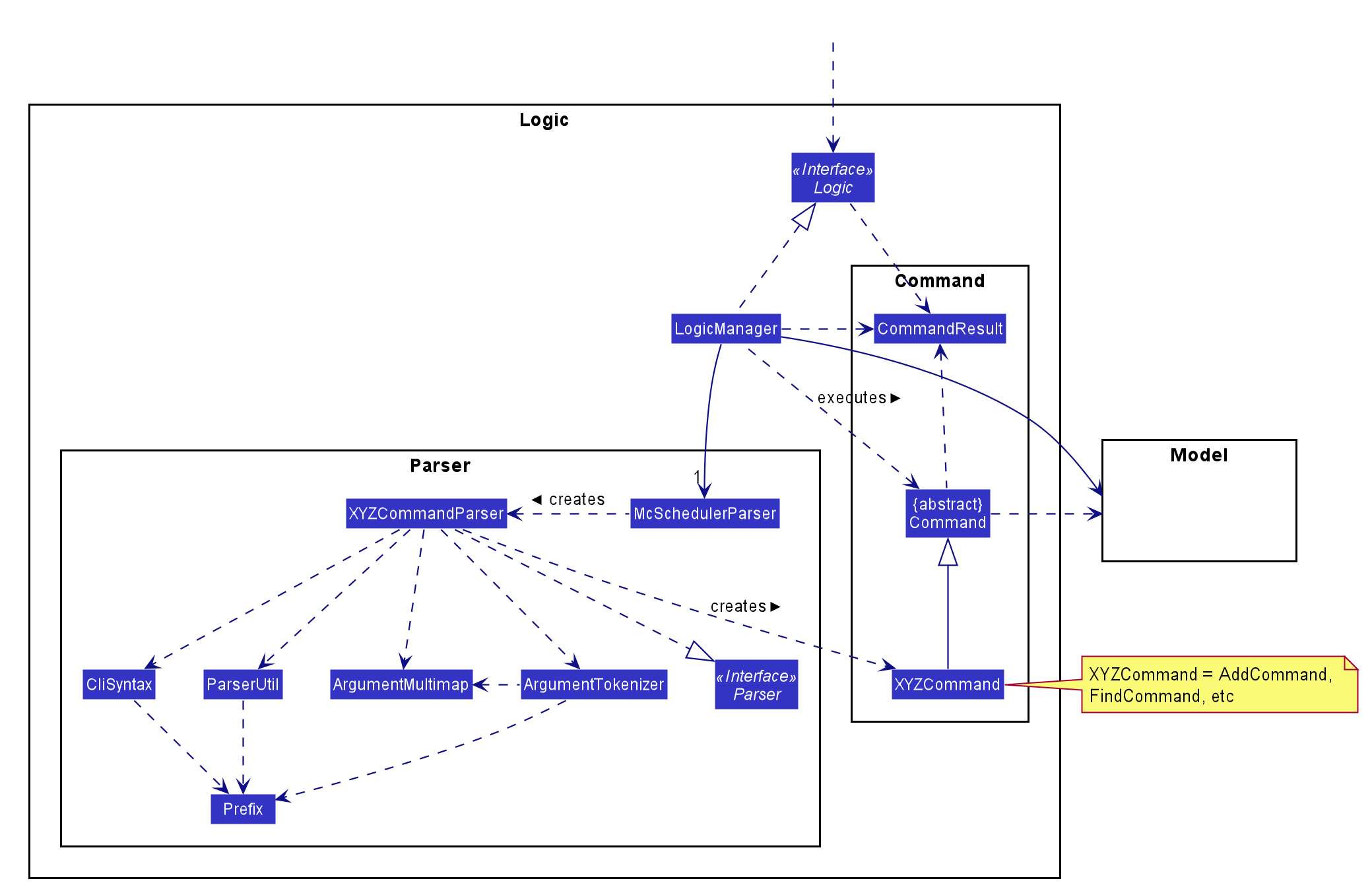
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command worker-delete 1.
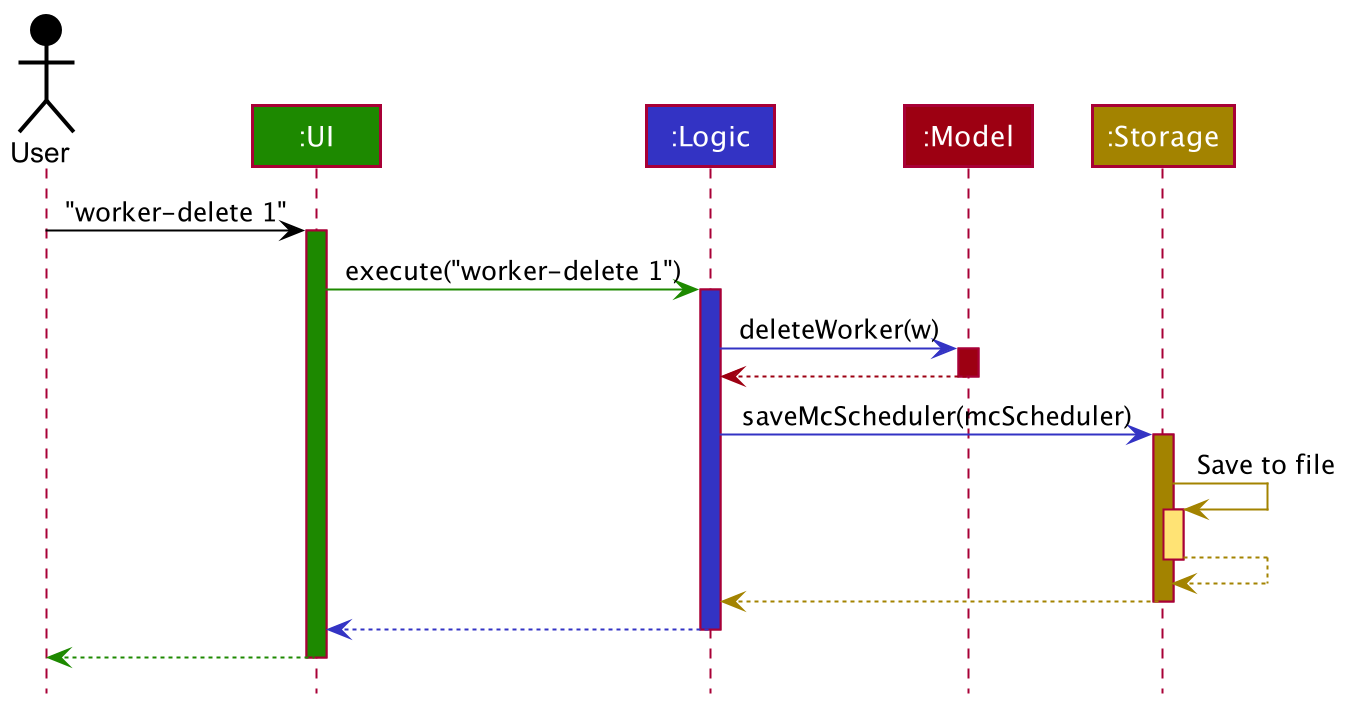
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
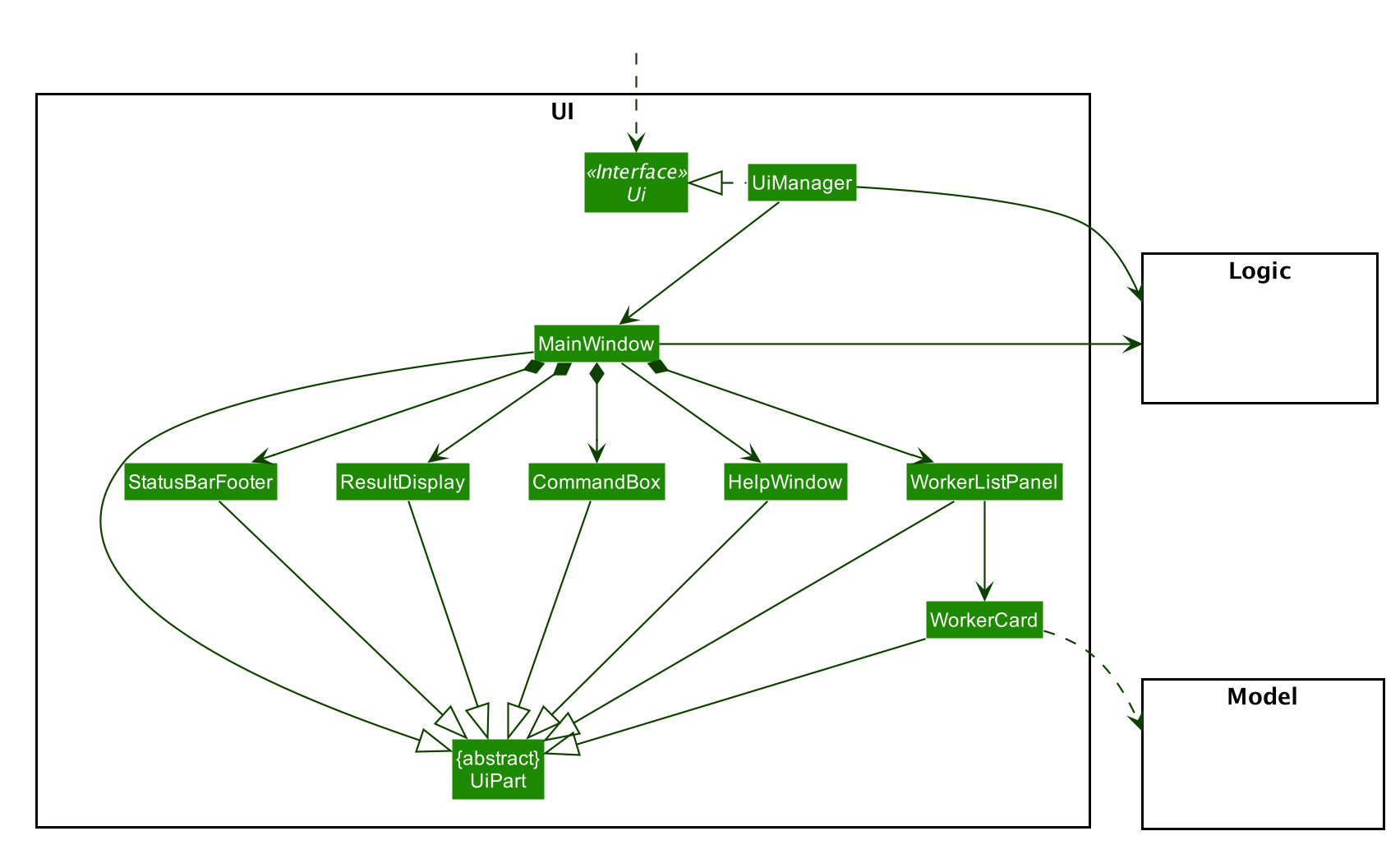
API :
Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, WorkerListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - Listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data.
Logic component

API :
Logic.java
-
Logicuses theMcSchedulerParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command execution can affect the
Model(e.g. adding a worker). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back to theUi. - In addition, the
CommandResultobject can also instruct theUito perform certain actions, such as displaying help to the user.
Given below is the Sequence Diagram for interactions within the Logic component for the execute("worker-delete 1") API call.
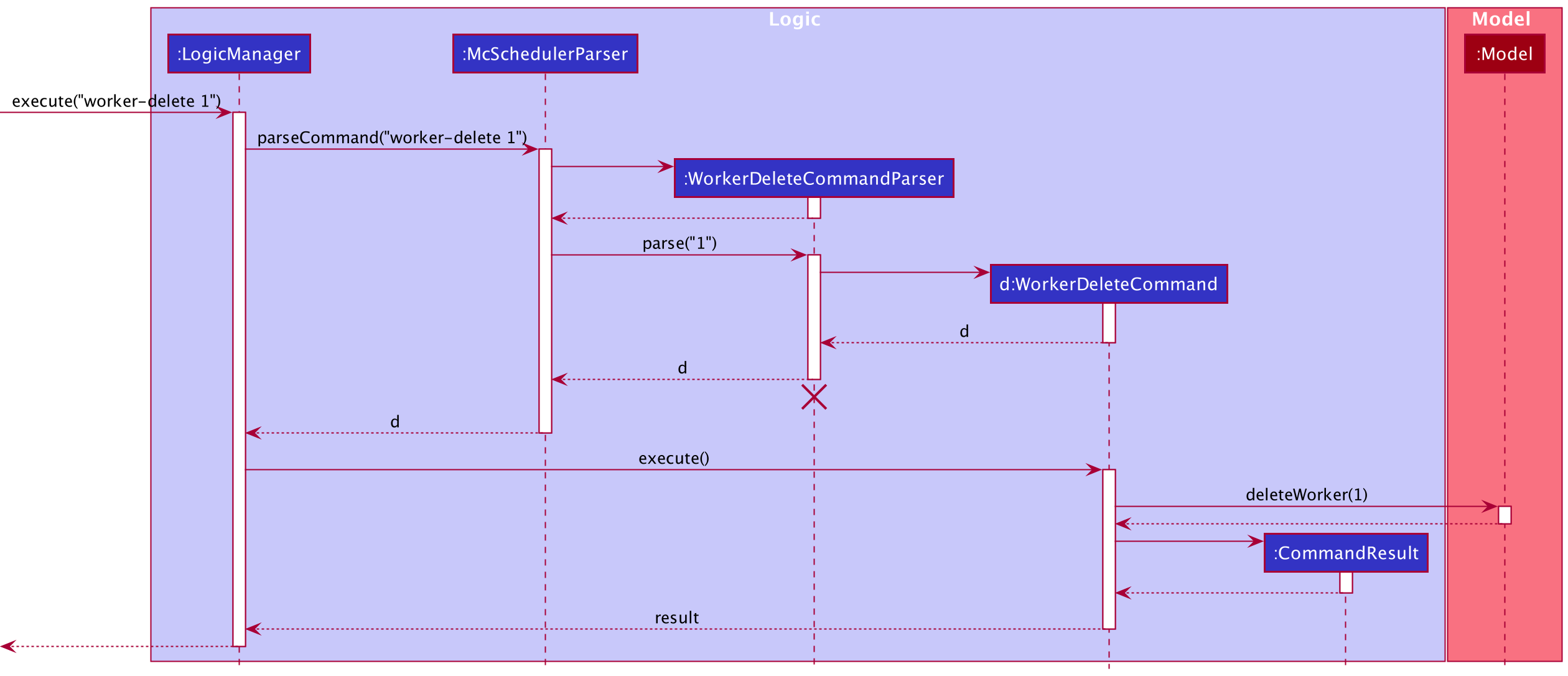
WorkerDeleteCommandParsershould end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Model component
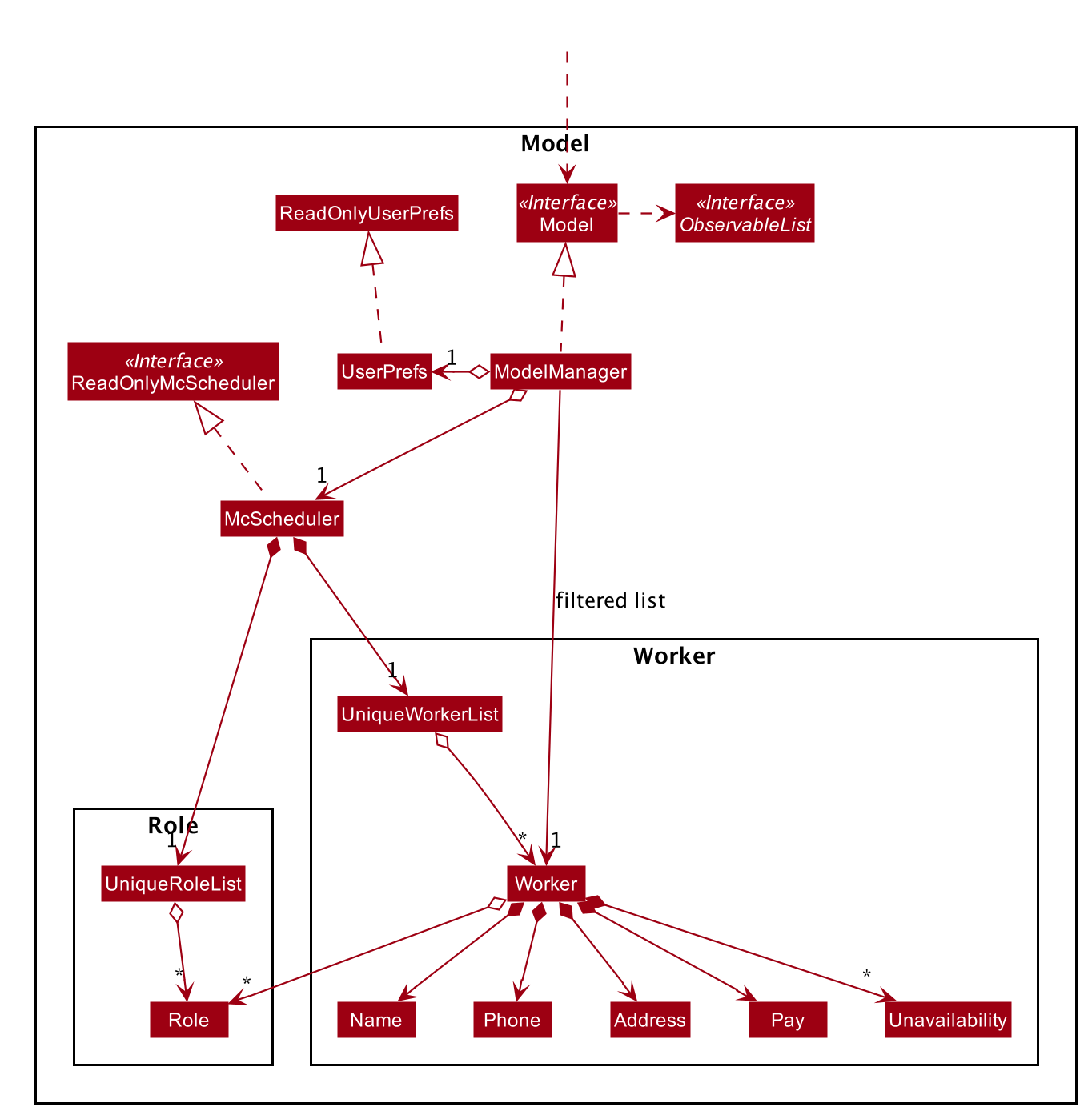
API : Model.java
The Model,
- stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. - stores the mcsheduler data.
- exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Worker>andObservableList<Role>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to these lists so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the lists change. - does not depend on any of the other three components.
Storage component
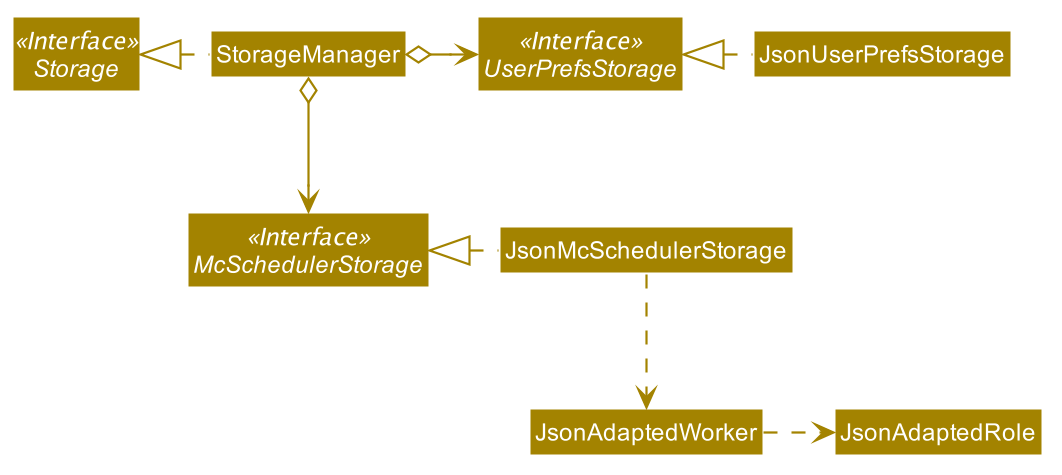
API : Storage.java
The Storage component,
- can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. - can save the mcscheduler data in json format and read it back.
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the mcscheduler.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Worker feature
The adding of workers is core to the functionality of the system. Users are able to add important information to each worker, which will help them assign workers to shifts they are most suited for.
Implementation
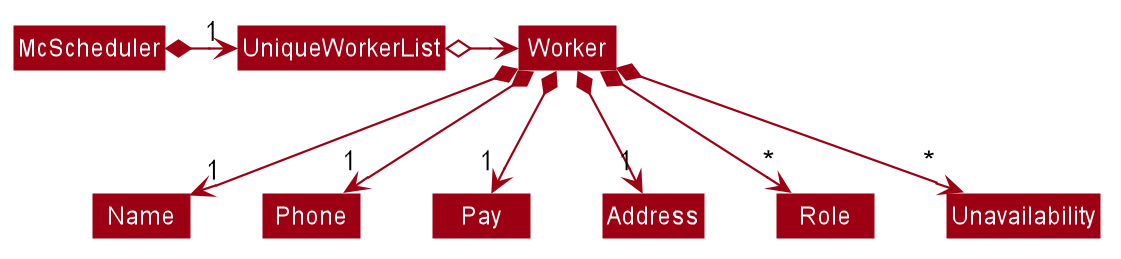
The mechanism for adding a worker is facilitated by a Worker class. A Worker has a Name, a
Phone, a Pay, an optional Role set and an optional Unavailability set.
A user can add a Worker to the McScheduler by running a worker-add command.
Example usage scenario
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the worker-add feature behaves at each step after the user has
launched the application.
Step 1. The user executes the command worker-add n/John hp/98765432 p/9.0 a/400 Scheduler Lane. McSchedulerParser
creates a WorkerAddCommandParser and calls the WorkerAddCommandParser#parse() method.
Step 2. The fields n/, hp/, p/, and a/ are parsed within WorkerAddCommandParser#parse() and an instance of
Name, Phone, Pay and Address are created respectively. These objects are passed as arguments to the Worker
constructor and a new Worker object is created.
Step 3. A WorkerAddCommand with the created Worker object as an argument is returned to the LogicManager and
executed. The Worker object is added to and stored inside the Model.
The following sequence diagram shows how Worker is added.
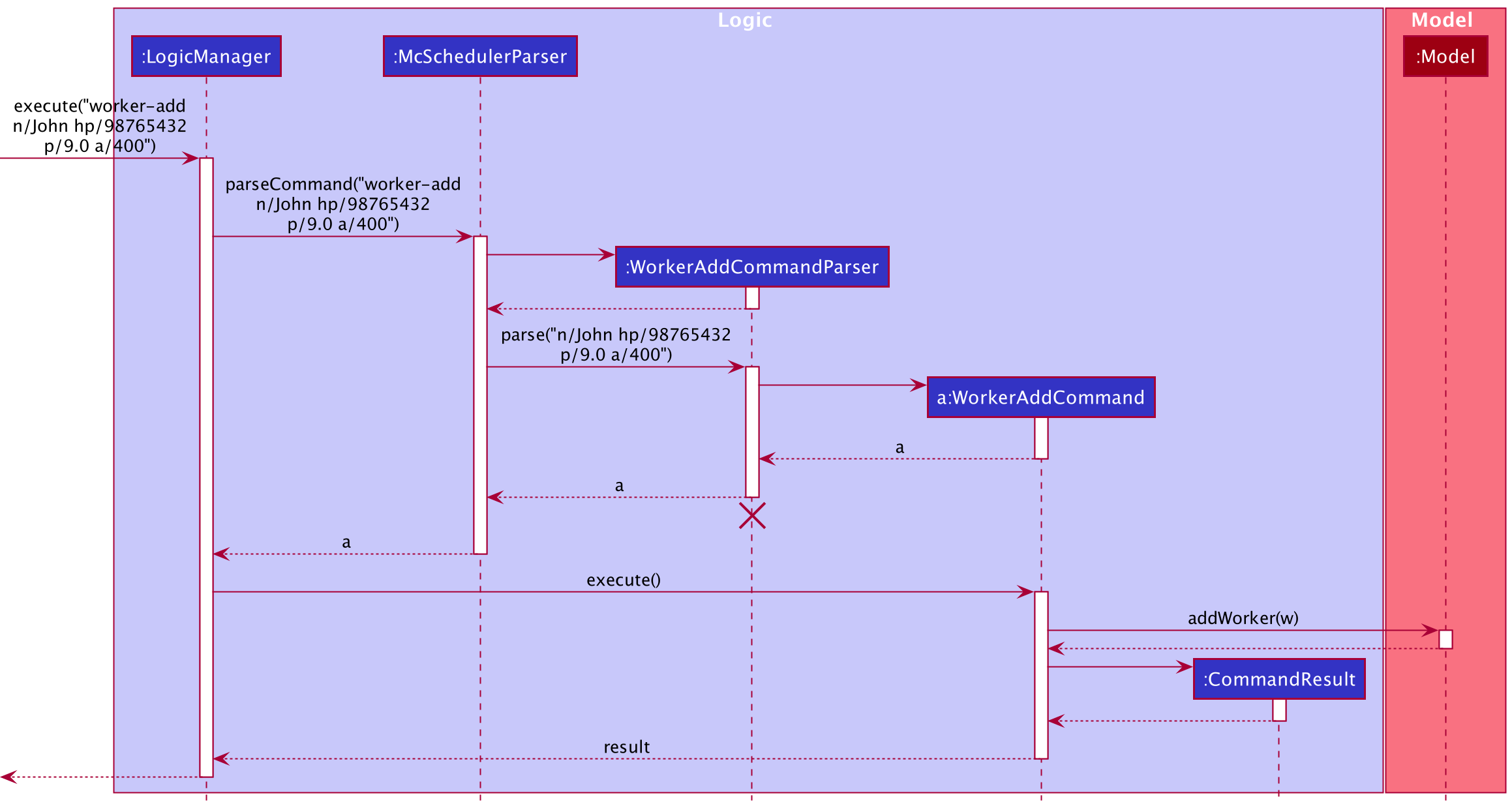
WorkerAddCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Shift feature
Similar to workers, adding and manipulating shifts is a key functionality of the McScheduler. Users will be able to add role requirements to shifts, assign workers to shifts and assign workers to take leave for a shift.
Implementation
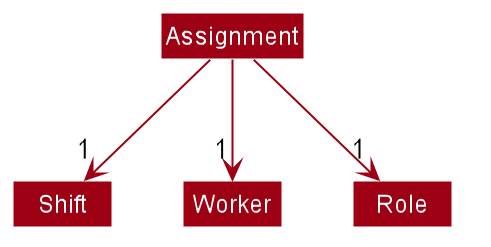
Shifts are represented by the Shift class. It contains important details related to shifts such as the day (through ShiftDay),
the time (through ShiftTime) and role requirements (through RoleRequirement) of the shift. A RoleRequirement object
details how many workers are needed to fill which roles in a given shift.
The following diagram details Shift and how it is represented in the App model.
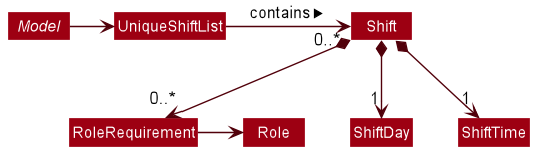
Commands
The following commands have been implemented to work with Shift:
-
ShiftAddCommandto add new shifts -
ShiftEditCommandto edit existing shifts -
ShiftDeleteCommandto delete existing shifts
These commands work similarly to the Worker based commands.
Example usage scenario
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the shift-edit feature works at each step.
Step 1. User enters the command shift-edit 2 d/FRI. McSchedulerParser creates a ShiftEditCommandParser and calls
the ShiftEditCommandParser#parser() method.
Step 2. The preamble index and field d/ are parsed within ShiftEditCommandParser#parser() and creates an instance of
ShiftEditCommandParser then creates a ShiftEditDescriptor with a new ShiftDay. Should there be other optional fields
such as ShiftTime or RoleRequirement as requested by the uder in their command, similar instances will be created and added
to the ShiftEditDescriptor.
Step 3. A ShiftEditCommand with the ShiftEditDescriptor and the index of the Shift of interest is returned and executed,
setting the edited shift within the model. This results in the replacement of the Shift object within the model with a newly
created Shift object based on the new attributes.
The following sequence diagram demonstrates this editing process (as per the example).
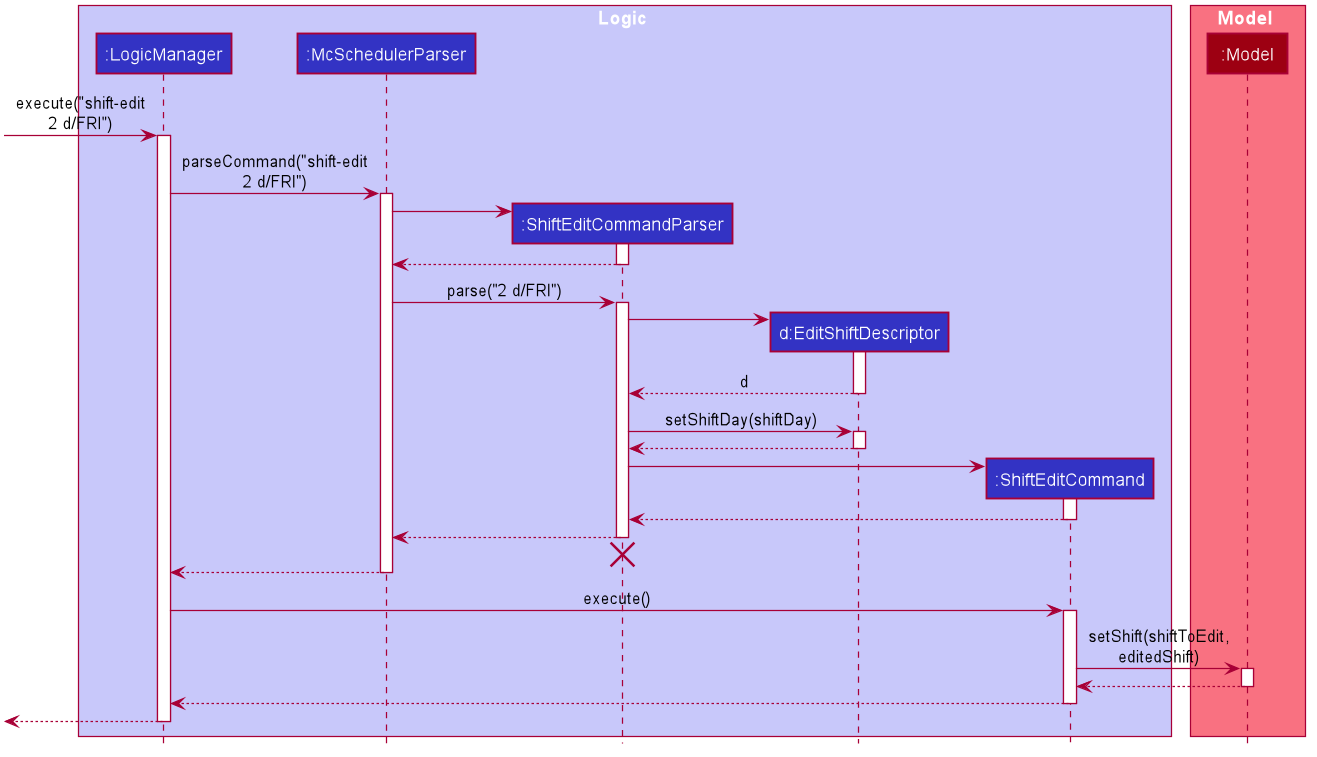
ShiftEditCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Should there be other information to be edited as requested by the user, there will be other objects created besides ShiftDay.
Unavailability feature
The unavailability feature allows users to add unavailable timings to a Worker, which comprise a day and/or a time.
The setting prevents workers from being assigned to shift slots that they are unavailable for.
Implementation
The proposed mechanism is facilitated by ParserUtil and the existing system for adding and editing workers.
Unavailability
Unavailability is represented by an Unavailability class. Since a worker’s unavailable timings are only relevant
in the context of existing shift slots, Unavailability contains a ShiftDay and a ShiftTime.
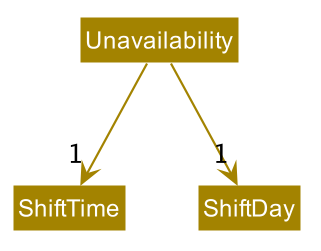
Instances of Unavailability can be created on 2 occasions:
- During a
worker-addcommand, prefixed withu/ - During a
worker-editcommand, prefixed withu/
To increase the efficiency of adding a worker’s unavailable timings, users may type u/UNAVAILABILITY_DAY to indicate a full-day unavailability
instead of typing u/UNAVAILABILITY_DAY AM and u/UNAVAILABILITY_DAY PM separately. Functionality has been added to support the creation
of an AM Unavailability and a PM Unavailability when u/UNAVAILABILITY_DAY is entered. The ParserUtil class supports this during parsing through:
-
ParserUtil#parseUnavailability()— Parses a String and creates a validUnavailabilityobject -
ParserUtil#createMorningUnavailabilityString()— Generates a String of the formatUNAVAILABILITY_DAY AM -
ParserUtil#createAfternoonUnavailabilityString()— Generates a String of the formatUNAVAILABILITY_DAY PM -
ParserUtil#parseUnavailabilities()— Iterates through a collection of Strings and creates anUnavailabilityobject for each
Example usage scenario
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the unavailability feature behaves at each step after the user has launched the application.
Step 1. The user executes a worker-add command worker-add ... u/Mon. McSchedulerParser creates a
WorkerAddCommandParser and calls the WorkerAddCommandParser#parse() method.
Step 2. Within WorkerAddCommandParser#parse(), ParserUtil#parseUnavailabilities() is called to generate an
Unavailability set from the given u/Mon field. ParserUtil#parseUnavailabilities() checks whether
the input contains only 1 keyword. In this case, since only 1 keyword (i.e. Mon) is present, ParserUtil#createMorningUnavailabilityString()
is called to generate a Mon AM String and ParserUtil#createAfternoonUnavailabilityString() is called to generate a Mon PM
String. Inside ParserUtil#parseUnavailabilities(), ParserUtil#parseUnavailability() is called on both Strings
and 2 valid Unavailability objects are created, before being added to the returnable Unavailability set.
Step 3. The Unavailability set is passed into the constructor of the Worker class to instantiate a Worker object
with the unavailable timings Mon AM and Mon PM.
The following sequence diagram shows how unavailable timings are added to a Worker.
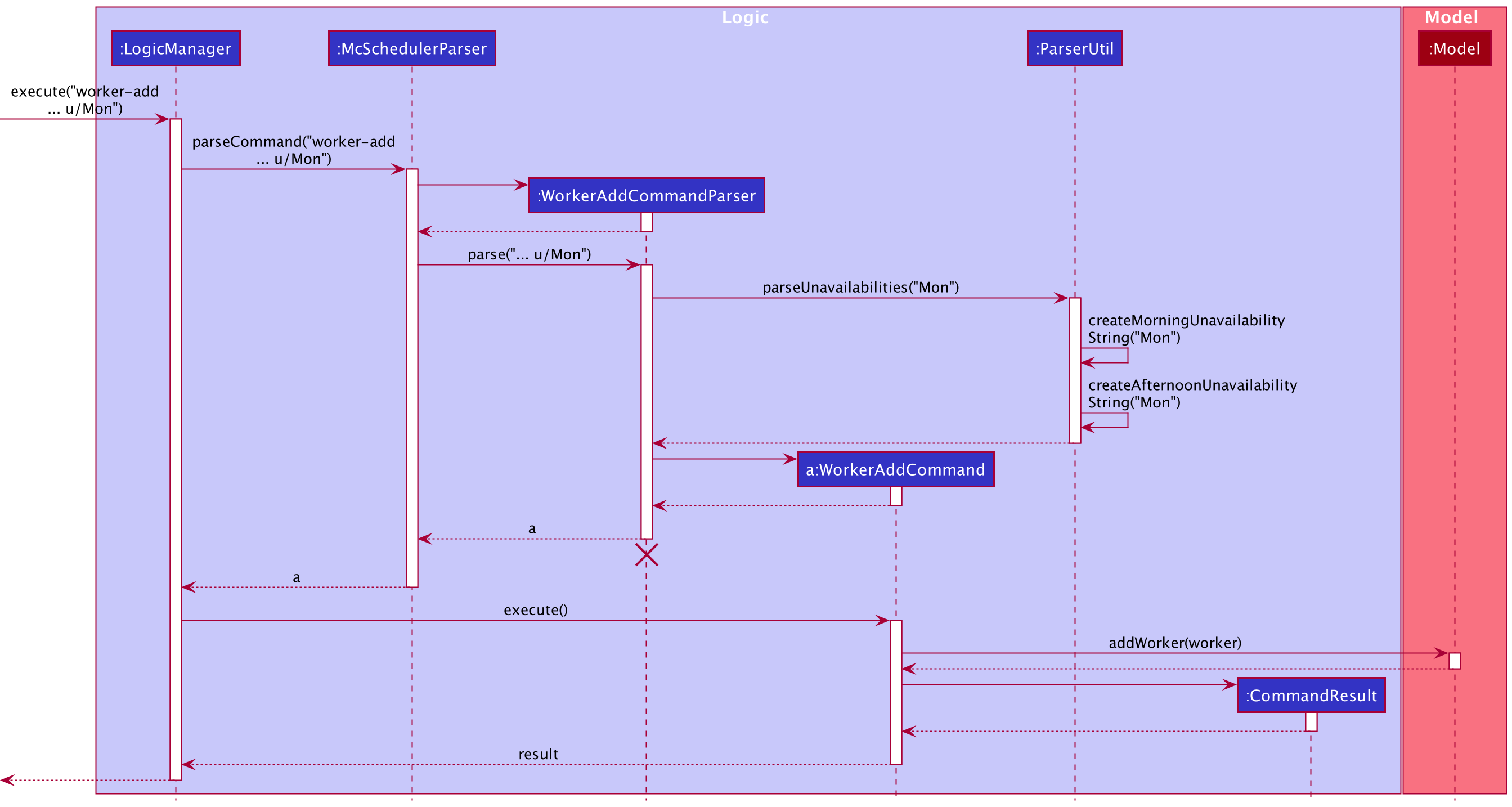
WorkerAddCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
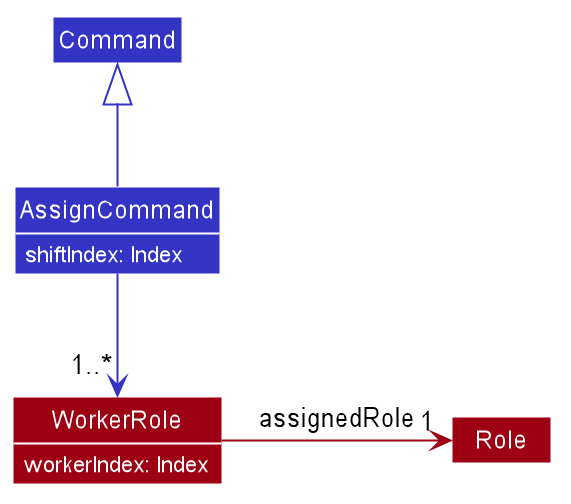
Assign/unassign feature
The assign/unassign feature allows the user to assign/unassign a worker to/from a role in a shift.
Implementation
This mechanism is facilitated by adding/deleting Assignment objects in the McScheduler. Each Assignment object
stores a Shift, Worker and Role object. The McScheduler maintains a UniqueAssignmentList, which enforces
uniqueness between Assignment objects by comparing them using Assignment#isSameAssignment(Assignment).
The operations supporting the adding/deleting of Assignment objects are exposed in the Model interface as
Model#addAssignment(Assignment) and Model#deleteAssignment(Assignment).
Example usage scenario
Step 1. The user executes assign s/1 w/1 Cashier to assign the 1st worker the role of a cashier in the 1st shift in
the McScheduler. McSchedulerParser creates an AssignCommandParser and calls the AssignCommandParser#parse() method.
Step 2. The fields s/ and w/ are parsed by the AssignCommandParser. A shiftIndex and Set<WorkerRolePair>
object are created respectively and passed as arguments into the AssignCommand constructor. The created AssignCommand
is executed in the LogicManager by calling the AssignCommand#execute() method.
Step 3. During the execution of the AssignCommand, an Assignment object, storing the 1st Shift, 1st Worker and cashier
Role objects, is created. The Assignment object is then added to the UniqueAssignmentList in the Model.
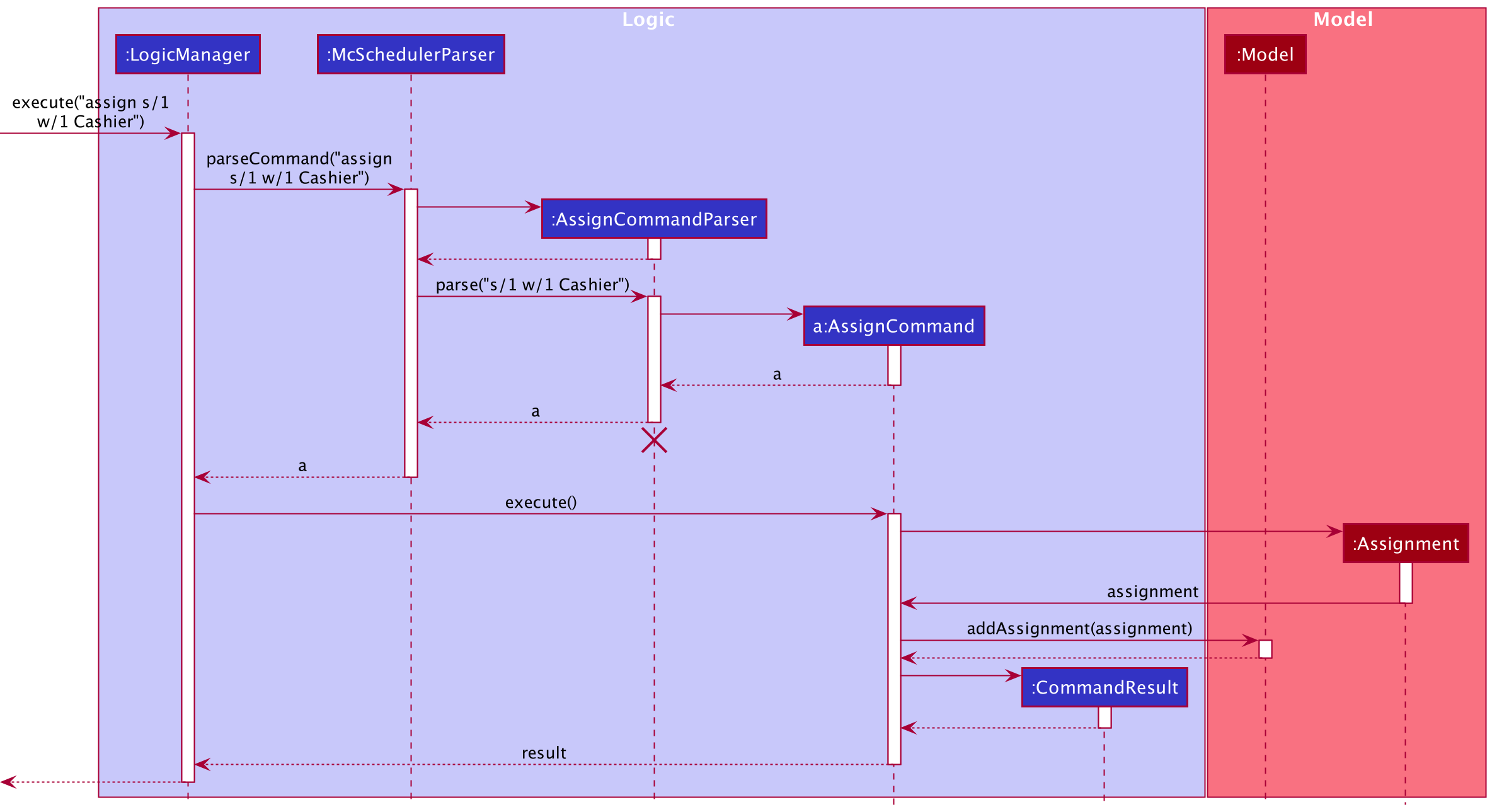
AssignCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Step 4. The user realises the previous command was a mistake and executes unassign s/1 w/1 to unassign the 1st worker
from the 1st shift in the McScheduler. The unassign command recreates the Assignment object to be deleted and uses it
as an identifier to identify the assignment to be deleted from the UniqueAssignmentList in the Model.
Role feature
The role feature allows users to add roles to a Worker and add RoleRequirement to a Shift. When assigning a Worker to a Shift under a particular Role,
we check that the Worker has the corresponding Role tagged to the Worker as the Role in the RoleRequirement of the particular Shift.
Implementation
The Role constructor takes in a String and creates a Role object with the according roleName. When tagging a Worker with a Role, we check that the Role is an allowed Role by checking if it exists in the
UniqueRoleList of the McScheduler.
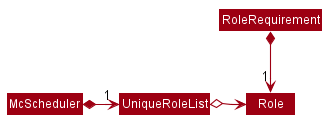
Commands
The following commands have been implemented to work with Role:
-
RoleAddCommandto add new roles toUniqueRoleList -
RoleDeleteCommandto delete existing roles inUniqueRoleList -
RoleListCommandto list existing roles inUniqueRoleList
Example usage scenario
Step 1. The user executes role-add Cashier to add the cashier role to the UniqueRoleList in the McScheduler ModelManager.
If the role being added already exists in the UniqueRoleList, DuplicateRoleException is thrown.
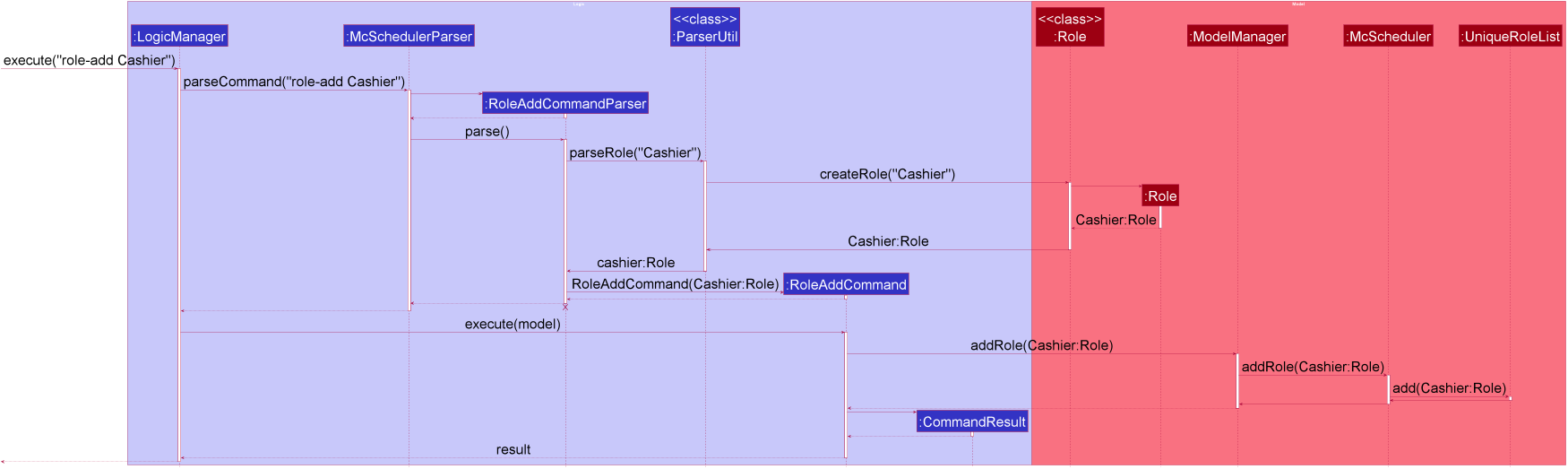
RoleAddCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Step 2. The user realises the previous command was a mistake and looks at the Role list to get the index of the cashier role in the UniqueRoleList.
Using the role index in the UniqueRoleList, the user executes role-delete ROLE_INDEX to remove the cashier role from the UniqueRoleList.
Take/cancel leave feature
The take/cancel leave feature allows users to set workers status to leave given a day and time. The setting prevents workers from being allocated to a work shift for which they are taking leave.
Implementation
The proposed mechanism to indicate that individuals are on leave makes use of the existing system for assigning workers to shifts with a particular role. By making use of the existing assignment system, certain conflicts can be avoided:
- Assignment of a worker to a shift when they took leave for that shift will not result in two assignments to the same shift.
Leave
Leave is represented as an extension of Role. To prevent conflicts between new Leave() and new Role("Leave"),
these two objects are deemed equivalent through Leave#equals() and Role#equals(). This implementation should
be reconsidered if there should be a significant difference between these two objects.
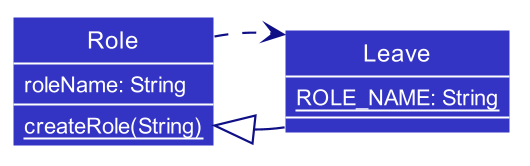
Due to their similarity, Leave objects are initiated using a common factory method as Role objects
through Role#createRole(), which will parse the given input as a Role or a Leave respectively.
This implementation prevents the creation of a role that has the same name as a leave.
To handle commands which should treat Leave differently as compared to other roles, Leave#isLeave() is provided.
Leave Assignment
Assignment makes use of the Assignment class features using Leave as the role.
Commands
Since Leave is essentially an extension of the assignment system, commands related to leave are very similar
to commands related to assignments.
-
TakeLeaveCommandsets workers to take leave for specific shift. It is a wrapper forAssignCommandandReassignCommand, depending on if the worker already is assigned for that shift. The following diagram demonstrates how this works.
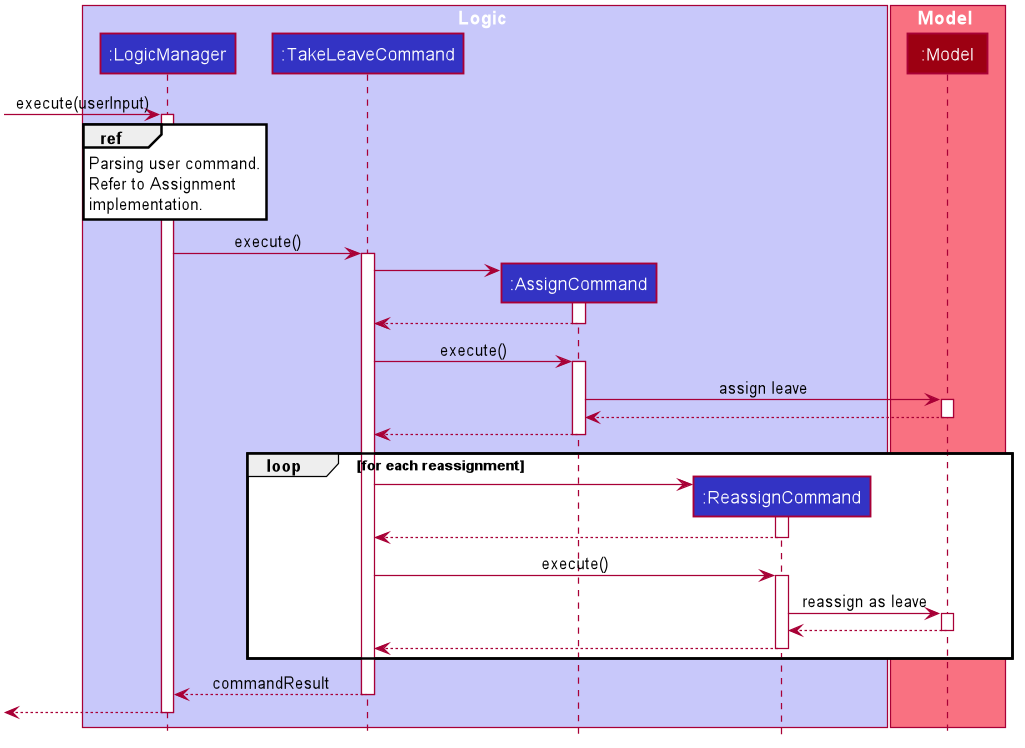
-
CancelLeaveCommandis very similar toUnassignCommand. However, there is a need to check if the assignment being removed represents a leave taken and not a normal role assignment. Hence,CancelLeaveCommandis implemented separately and not as a wrapper. However, its implementation details is almost identical toUnassignCommand.
For more information, see Implementation for Assign/Unassign Feature.
Mass Operation Commands
To increase the convenience of use for our expected typist user, we introduced a few mass operations related to leave:
-
TakeLeaveCommandandCancelLeaveCommandboth allow for many worker to one shift leave assignment similar toAssignCommandandUnassignCommand. See MassOps Implementation Details. -
MassTakeLeaveCommandandMassCancelLeaveCommandallow for one worker to many shift-leave assignment.- These two mass commands allow for taking leave over a range of days - similar to how leave is often planned by workers.
- These two commands do not require
Shifts representing the range of days and times to take leave to be present. A bare-bonesShiftwith onlyShiftDayandShiftTimewill be initialised for eachShiftthat has no identity equivalent (viaShift#isSameShift())Shiftpresent in the McScheduler. - The two commands handle other
Assignments differently:-
MassTakeLeaveCommandinforms the user after the command is complete if the worker is already scheduled for a shift (i.e. a non-leaveAssignment). TheAssignmentis replaced to indicate the leave taken. -
MassCancelLeaveCommandsearches for leaves in the datetime range and ignores non-leaves.
-
The following activity diagram describes the process behind MassTakeLeaveCommand.
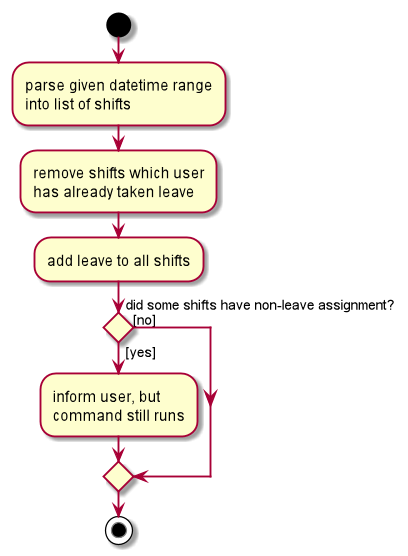
Future Extensions - Leave Quota
The following leave quotas could be implemented, possibly using the existing RoleRequirement class:
- Quota of leave per worker
- Quota of leave per shift
MassOps Feature
For certain commands that will be frequently used (assign, unassign, take-leave, cancel-leave), mass
operations are supported to reduce the required number of command calls.
Implementation
These operations consist of their own *Command class and *CommandParser class. In each of the supported
*CommandParser class, mass operations uses the ArgumentMultimap#getAllValues(Prefix) method, which parses the
user input and returns all values that start with the specific prefix. In this case, the prefix is ‘w/’,
signifying a Worker-Role relation.
Once the Command object has its shiftIndex and Set of WorkerRole, it creates individual Assignments and adds
them to the Model.
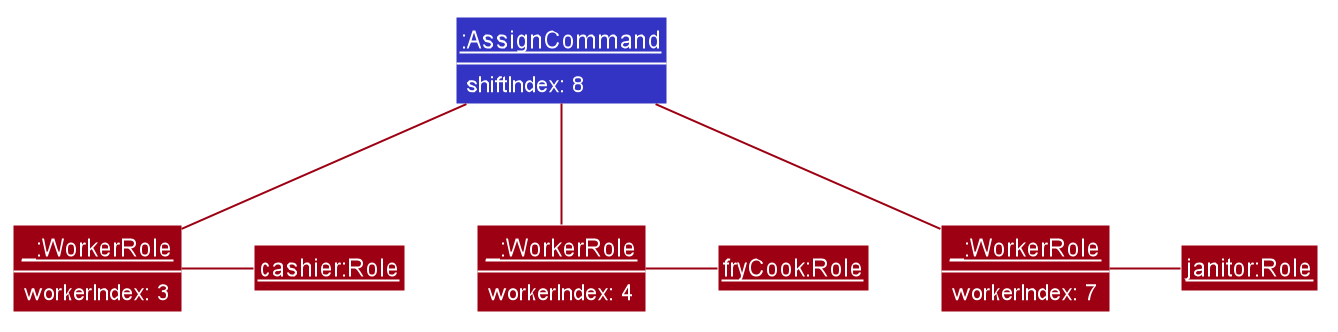
Example usage scenario
Let’s say that the manager has a new Shift, and requires 3 of their existing staff members to work on that shift immediately.
Step 1. The manager creates a new Shift through the shift-add command if it was not already done.
Step 2. The manager calls assign to assign the 3 existing Workers to the Shift.
eg. assign s/8 w/2 Cashier w/3 Fry Cook w/7 Janitor to assign Workers 2, 3, and 7 to the Role of Cashier, Fry Cook,
and Janitor respectively to Shift 8.
Step 3. McScheduler parses the input and creates 3 Assignments, which are then added to the Model:
- Shift 8, Worker 2, Cashier
- Shift 8, Worker 3, Fry Cook
- Shift 8, Worker 7, Janitor
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- is a McDonald’s shift manager in Singapore
- manages a significant number of worker contacts
- manages a large number of work shifts
- prefers desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: McScheduler is a one-stop solution for McDonald’s shift managers to manage shift scheduling, as well as worker contacts and compensation. All relevant information is easily available to help streamline the management process. It is also easy for the manager to contact workers, and manage their hours and pay. McScheduler aims to be faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app for fast typists.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
Worker-related stories
-
* * *As a user, I want to add a new worker and their details, so that I can track the worker’s data and schedule their work -
* * *As a user, I want to view a list of all workers, so that I can know who are the workers I can assign shifts to
- [Epic]
* * *As a user, I want to view the details of a worker-
* * *As a user, I want to view the contact details of workers, so that I can contact them easily -
* * *As a user, I want to view the roles a worker can fill, so that I can assign them a role they are fit for -
* * *As a user, I want to view the shifts a worker is unavailable or has taken leave for, so that I can assign them only shifts they are available for -
* * *As a user, I want to view the shifts a worker is already assigned to, so that I can assign them only shifts they have not been assigned to -
* *As a user, I want to find a specific worker among all other workers, so that I can easily view their details without sieving through the whole list of workers -
* *As a user, I want to view the weekly pay of a worker, so that I can compensate them accordingly
-
-
* *As a user, I want to edit the details of a worker, so that I can have the most up-to-date information for shift scheduling and if I need to contact them -
* * *As a user, I want to delete a worker, so that I can remove a worker who has left McDonald’s -
*As a user, I want to see a worker’s service rating, so that I can decide who to give more work opportunities to
Shift-related stories
-
* * *As a user, I want to add a new shift, so that I can assign workers to shifts -
* * *As a user, I want to add roles and the respective quantities that need to be filled to a shift, so that I can assign workers based on what is needed -
* * *As a user, I want to view a list of all shifts, so that I can have an overview of all the shifts I am managing - [Epic]
* * *As a user, I want to view the details of a shift-
* * *As a user, I want to view the roles and their quantities required in a shift, so that I can assign workers based on what is needed -
* * *As a user, I want to view the workers already assigned to a shift and the role they are filling, so that I can know which roles have yet to be filled -
* *As a user, I want to view all workers available to fill a role in a shift, so that I can more easily assign workers shifts -
* *As a user, I want to find a specific shift among all other shifts, so that I can easily view its details without sieving through the whole list of shifts
-
-
* *As a user, I want to edit the details of a shift, so that I can reflect any changes in the timing, roles or number of workers needed for the shift -
* * *As a user, I want to delete a shift, so that I can remove an unwanted shift
Assignment-related stories
-
* * *As a user, I want to assign a worker to a role in a shift, so that I can fill shift positions -
* *As a user, I want to edit an existing assignment, so that I can easily move workers around after assigning them to a role in a shift -
* * *As a user, I want to unassign a worker from a shift, so that I can update the quantity of the role that has been and has yet to be filled -
* *As a user, I want to generate a weekly shift schedule, so that I can see at a glance the workers assigned to every shift in the week
General stories
-
* *As a new user, I want to see sample data, so that I can see what I can do with the app -
* *As a new user ready to add my own data, I want to delete all sample data, so that all data in the app is relevant to me -
* *As a new user, I want to see a guide on how to use the key functions, so that I can learn how to use the app -
* *As a user, I want to see a summary of the various commands, so that I can easily refer to it when I forget the exact format for the commands
Some user stories are to be implemented beyond v1.4
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the McScheduler and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise).
Use case: Add a worker (UC-001)
MSS
- User requests to add worker.
-
McScheduler adds worker.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The given worker information has missing or wrong data.
-
1a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Delete a worker (UC-002)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to delete a specific worker in the list.
-
McScheduler deletes the worker.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Edit a worker’s information (UC-003)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to edit a specific worker in the list.
-
McScheduler edits the worker.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
-
3b. No information is given or the information is invalid.
-
3b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Add a shift (UC-004)
MSS
- User requests to add a shift.
-
McScheduler adds the shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The shift information is missing or invalid (wrong values).
-
1a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Delete a shift (UC-005)
MSS
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to delete a specific shift on the list.
- McScheduler deletes the shift.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Edit a shift’s information (UC-006)
MSS
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to edit a specific shift in the list.
-
McScheduler edits the shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
-
3b. No information is given or the information is invalid.
-
3b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Assign a worker to a shift (UC-007)
MSS
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to assign worker at a specific position on the workers’ list to a shift at a specific position on the shifts’ list for a given role.
-
McScheduler assigns specified worker to specified shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of shifts is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
5a. At least one of the given indexes are invalid.
-
5a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5b. The worker is unable to fulfil any role required for given shift.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5c. The worker is unavailable on the day and time of the shift.
-
5c1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5d. The worker is on leave for the shift.
-
5d1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5e. The given role is not registered in the McScheduler.
-
5e1. McScheduler shows an error message.
-
5e2. User adds the given role to the McScheduler as a new role (UC-012).
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5f. The worker is already assigned to the shift under the same role.
-
5f1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5g. The worker is already assigned to the shift under a different role.
-
5f1. McScheduler shows an error message.
-
5f2. User reassigns worker to a different role for the same shift (UC-017)
-
Use case: Unassign a worker from a shift (UC-008)
MSS
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to unassign worker at a specific position on the workers’ list to a shift at a specific position on the shifts’ list.
-
McScheduler unassigns specified worker from specified shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of shifts is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
5a. At least one of the given indexes are invalid.
-
5a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5b. The worker is not assigned to the given shift.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
-
5b. The worker is on leave for the given shift.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use Case: Hire a new worker for shifts (UC-009)
MSS
- User adds a worker (UC-001).
-
User assigns worker to a shift (UC-007).
Step 2 is repeated for all shifts the worker is hired for.
Use case ends.
Use case: Calculate the pay earned by a worker for the week (UC-010)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to calculate the pay earned for the week by a worker at a specific position on the workers’ list.
-
McScheduler shows the pay earned by the specified worker for the week.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The worker index given is invalid.
-
3a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: View the list of workers who are available to work for a given shift under a given role (UC-011)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to view the list of workers who are available to work for a shift at a specific position on the shifts’ list under a given role.
-
McScheduler shows the list of available workers who are available to work for the specified shift under the specified role.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. The list of shifts is empty.
Use case ends.
-
5a. The shift index given is invalid.
-
5a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5b. The role given is not registered in the McScheduler.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
-
5b2. User adds the given role into the McScheduler as a new role (UC-012).
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
Use case: Add a new role into the McScheduler (UC-012)
MSS
- User requests to create new role.
-
McScheduler shows a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The role name of the new role contains non-alphanumeric characters.
-
1a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Delete a role from the McScheduler (UC-013)
MSS
- McScheduler shows a list of roles.
- User requests to delete the role at the specific position on the roles’ list.
-
McScheduler deletes the role.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list of roles is empty.
Use case ends.
-
2a. The role index given is invalid.
-
2a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: Edit an existing role in the McScheduler (UC-014)
MSS
- McScheduler shows a list of roles.
- User requests to edit a role at a specific position on the roles’ list.
-
McScheduler edits the role.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The list of roles is empty.
Use case ends.
-
2a. The role index given is invalid.
-
2a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
-
2b. The new role name contains non-alphanumeric characters.
-
2b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: Take leave for a worker for a given shift (UC-015)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to take leave for a worker at a specific position on the workers’ list for a shift at a specific position on the shifts’ list.
-
McScheduler takes leave for the specified worker for the specified shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. The list of shifts is empty.
Use case ends.
-
5a. At least one of the given indexes are invalid.
-
5a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5b. The specified worker is already on leave for the specified shift.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
-
5c. The worker is unavailable on the day and time of the shift and does not need to take leave.
-
5c1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
Use case: Cancel leave for a worker for a given shift (UC-016)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to cancel leave for a worker at a specific position on the workers’ list for a shift at a specific position on the shifts’ list.
-
McScheduler cancels leave for the specified worker for the specified shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. The list of shifts is empty.
Use case ends.
-
5a. At least one of the given indexes are invalid.
-
5a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5b. The specified worker is not on leave for the specified shift.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Reassign the worker to a different role for a given shift (UC-017)
MSS
- User requests to list workers.
- McScheduler shows a list of workers.
- User requests to list shifts.
- McScheduler shows a list of shifts.
- User requests to reassign a worker at a specific position on the workers’ list to a different role for a shift at a specific position on the shifts’ list.
-
McScheduler reassigns the specified worker to a different role for the specified shift.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list of workers is empty.
Use case ends.
-
4a. The list of shifts is empty.
Use case ends.
-
5a. At least one of the given indexes are invalid.
-
5a1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 4.
-
-
5b. The specified worker is on leave for the specified shift.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
-
5b. The specified worker is not assigned to the specified shift under any role.
-
5b1. McScheduler shows an error message.
Use case ends.
-
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 workers and 1000 shifts without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- Should be able to save up to 1000 workers and 1000 shifts worth of data that persists over sessions.
- Data should be saved after every change.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- A fresh new user should be able to figure out how to use the app easily.
Glossary
- Assignment: A shift and role allocation to a particular worker, where the worker is given a particular role in the particular shift (e.g. An assignment can involve a worker A, who is a Chef in shift B)
- Leave: A worker’s day-off, where the worker will not be available for work for that particular day
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, macOS
- Role: A position that a worker is able to fill based on their skill set (e.g Cashier, Cleaner, Burger Flipper)
- Role requirement: A role and the corresponding number of workers that is required to fill that role in a shift
- Service Rating: A rating given based on how well the worker performs at their work
- Unavailability: A particular day and time (e.g. “Monday AM”) where a particular worker is unavailable for work on a recurring basis (e.g. A worker whose unavailability is “Monday AM” is unavailable for work every Monday morning)
- Worker role pair: A worker and the corresponding role they will be assigned to
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
Deleting a worker
-
Deleting a worker while all workers are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all workers using the
worker-listcommand. Multiple workers in the list. -
Test case:
worker-delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. -
Test case:
worker-delete 0
Expected: No worker is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
worker-delete,worker-delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
Saving data
-
Dealing with missing data files
-
To simulate missing data files, delete
./data/mcscheduler.json. -
Start up McScheduler.
Expected: When no data file is detected, McScheduler will automatically populate the App with sample data. This consists of 6 workers, 3 roles and 2 shifts.
-
-
Dealing with corrupted data files
-
To simulate corrupted data files, edit
./data/mcscheduler.jsonby replacing"workers"in the property to something else (e.g."employees"). -
Start up McScheduler.
Expected: No data will be displayed. An error message will be displayed advising users to fix the data file or delete it to get sample data.
-